
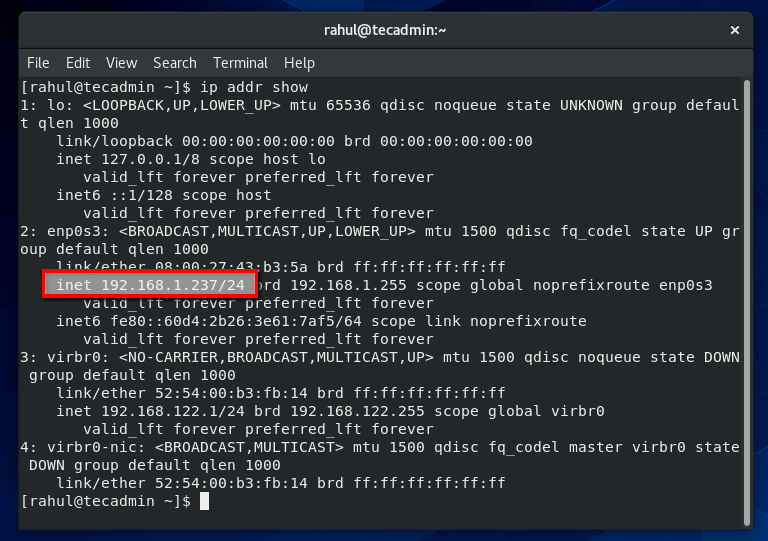
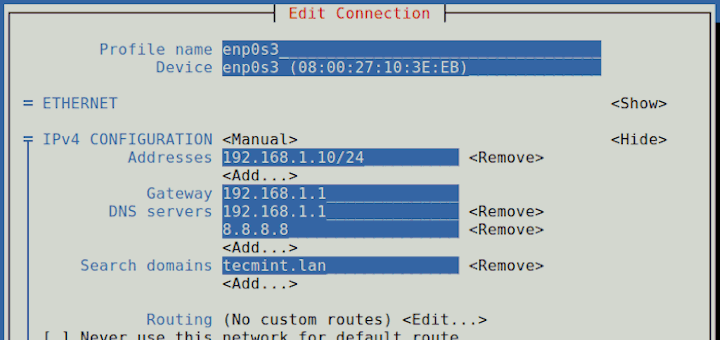
Feel free to get back to us for any clarifications. Your thoughts about this article are highly welcome. Verify the settings using ifconfig command and cat /etc/nf Wrapping up To configure a static IP, remove DHCP and append ‘static’ to ‘inet’ and enter your preferred address, netmask, gateway and dns-name servers auto eth0 Navigate to the network interface configuration file nano /etc/sysconfig/interfaces Hit edit.Ĭonfiguring a static IP in Ubuntu 14.04, 16.04 Press ‘Tab’ key to navigate to the other options. It can be installed both on RPM and Debian based distributions.įor Centos & RHEL 7 yum install NetworkManager-tui dnf install NetworkManager-tui For Fedora 21 and later Nmtui, short for Network Manager Text User interface is a GUI tool that painlessly allows you to configure your network interface without having to touch the command line. Restart the networking service systemctl restart networkĪlso, check the nameservers cat /etc/nf To set a static IP, modify the following settings: HWADDR=08:00:27:1d:2a:e1 This tells the system to start networking service at boot time. The sample output should contain the following parameters: NETWORKING=yes Navigate to the following path to view interface statistics of interface enp0s3 vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp0s3 TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0Ībove, we can observe that our IP address is 192.168.43.160 and netmask is 255.255.255.0 We are going to configure this statically. Configuring a static IP in Fedora 27, CentOS and RHEL 7įirstly, list the IP of all interfaces ifconfig -a
Let’s see how we can configure a static IP in different distros. This will definitely cause loss of service once the IP changes. You definitely don’t want its IP to keep changing once the DHCP lease time is over. A good example is where you have a server, e.g a web server or an FTP server. However, there are certain instances that require configuration of a static IP. This implies that it automatically obtains an IP address from a router or a DHCP server in a network.

By default, upon installation, any Linux system uses DHCP for its network configuration.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
